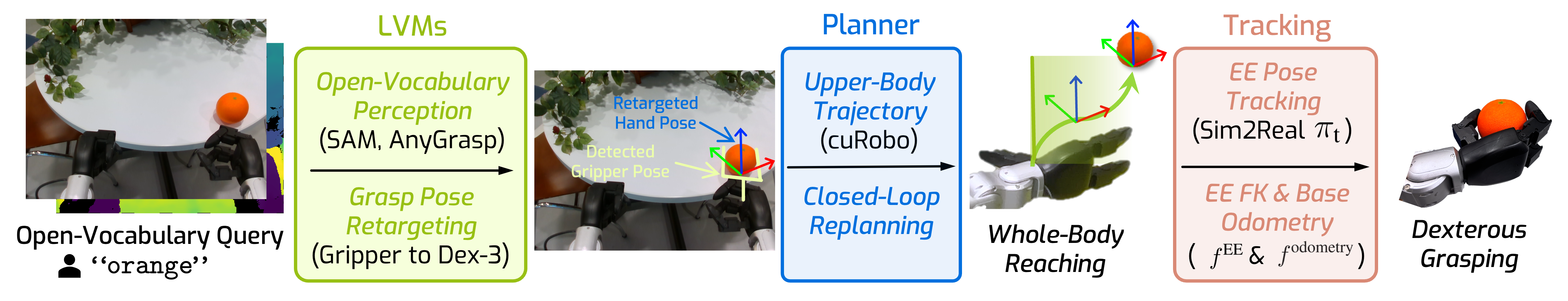
Autonomous novel object grasping in novel scenes: The robot autonomously loco-manipulates novel objects in novel scenes using onboard sensors only, first achieving open-vocabulary object loco-manipulation without any human demosntrations.
 "red apple"
"red apple"
 "red coke can"
"red coke can"
 "emergency stop button"
"emergency stop button"
 "orange cube"
"orange cube"
 "olive oil bottle"
"olive oil bottle"
 "game cartridge"
"game cartridge"
 "chip can"
"chip can"
 "hand soap bottle"
"hand soap bottle"
 "robot hand"
"robot hand"
 "red piranha plant"
"red piranha plant"
End-to-end testing on 10 daily objects: The robot successfully grasps and lifts a wide variety of objects with different shapes, sizes, and materials, demonstrating its ability to generalize across diverse object categories and physical properties without any object-specific fine-tuning.
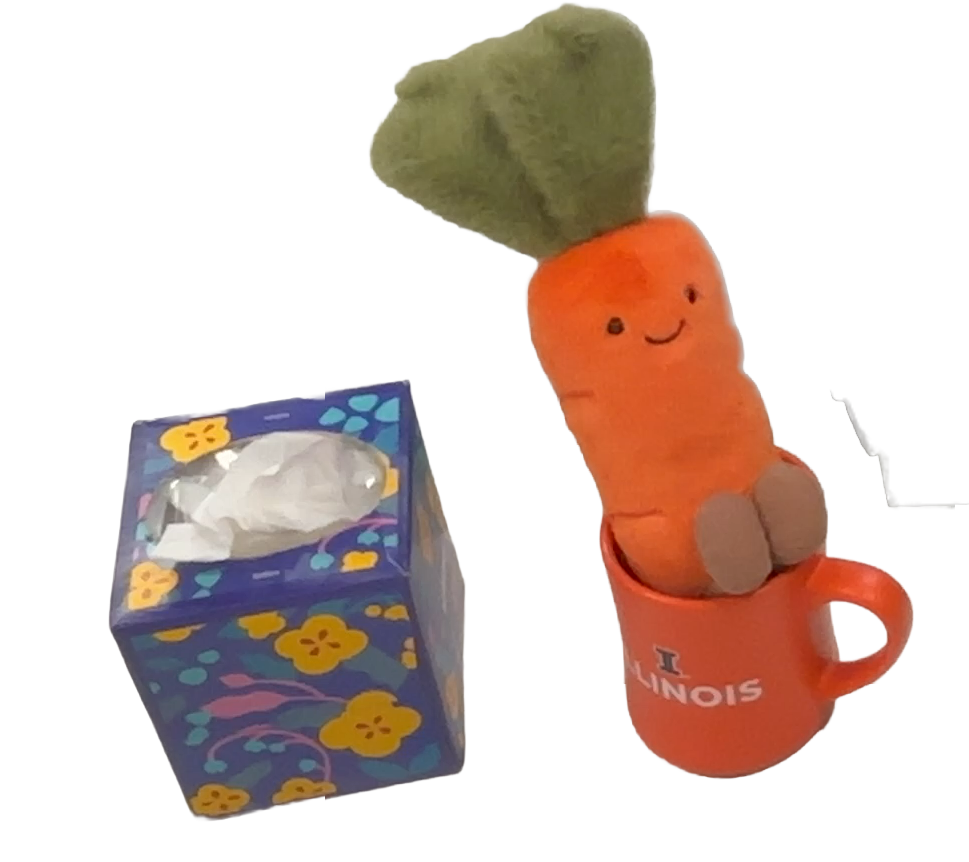 "carrot"
"carrot"
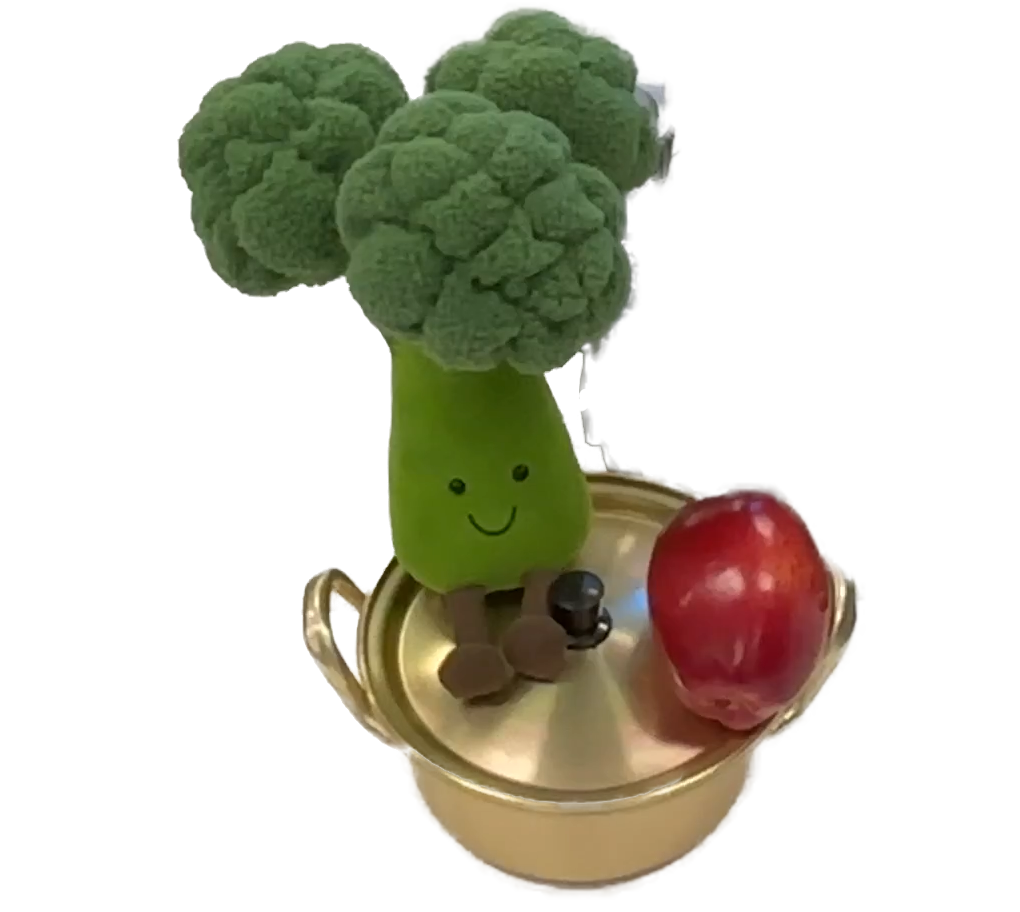 "broccoli"
"broccoli"
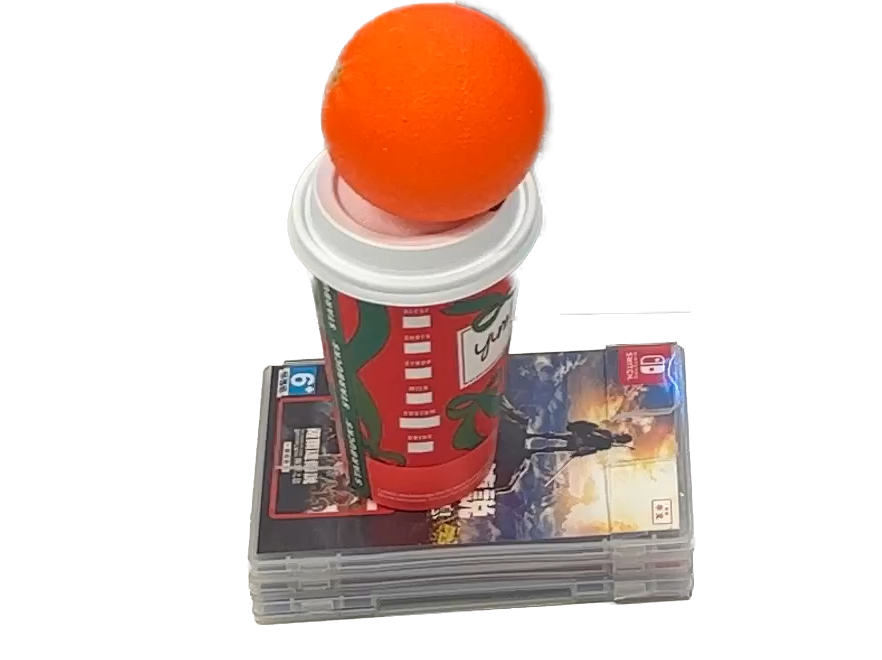 "orange"
"orange"
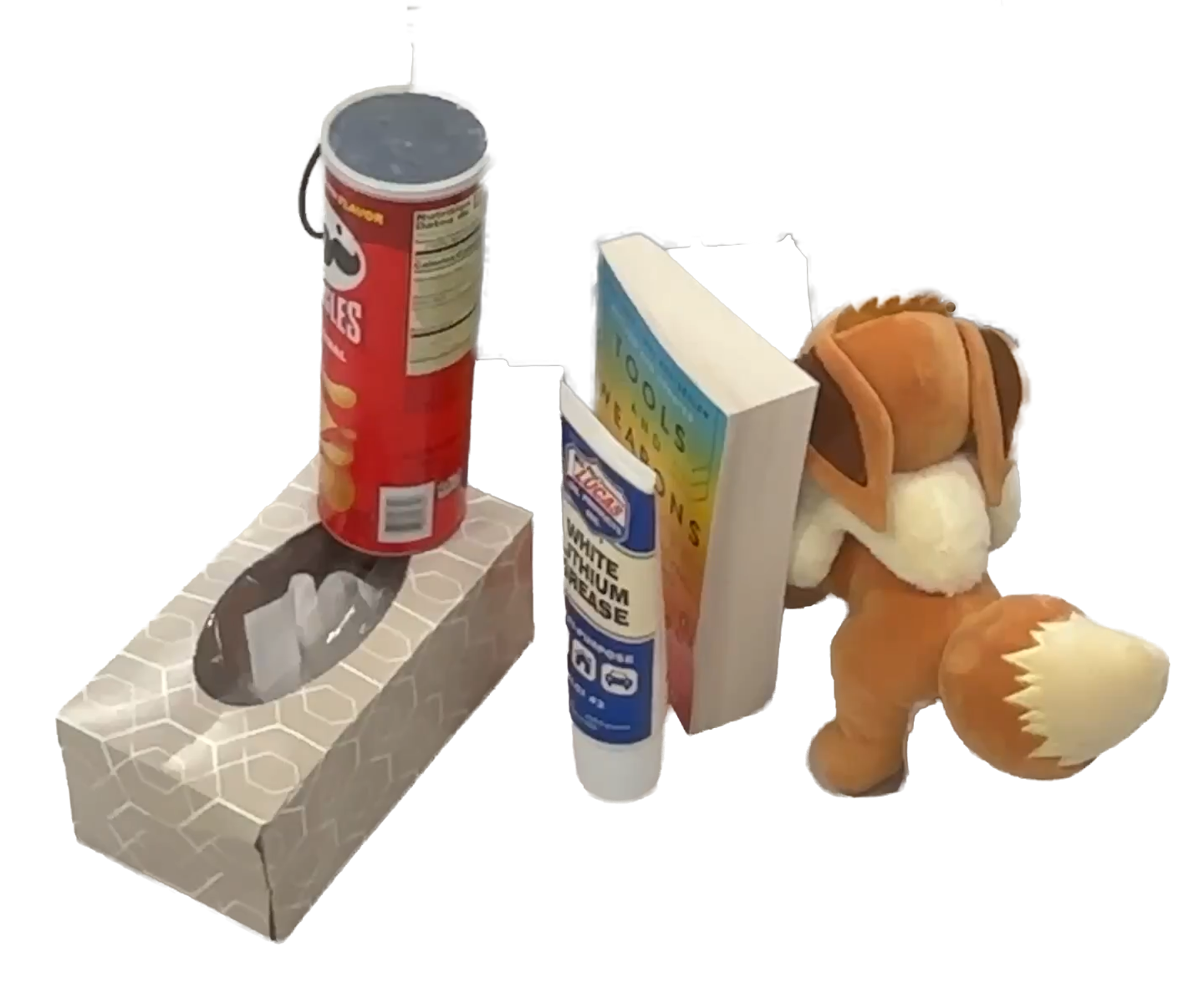 "chip can"
"chip can"
 "book"
"book"
Clutterred scenes: The robot successfully grasps the target object from cluttered scenes with various layouts, demonstrating its ability to handle occlusions and distractions in complex environments.
Red Apple Location: The robot successfully grasp the red apple from various locations and layouts on the table.
Replanning from vision: For moving objects, the robot can successfully replan from vision.
Easy extension to door opening: The robot successfully opens a door via first grasping the door handle and then return the default pose.
Walk and Grasp: The robot keeps walking forward until it sees the target object and stops for grasping. However, it indicates that the egocentric field of view is limited and the robot can only see objects when getting very close to objects.
Failure Modes: Besides the failure modes shown in trial videos, here we show some more failure cases that we observed during testing. These failure comes from object slipping, hand getting stuck, unstable grasp on plushy or heavy objects.
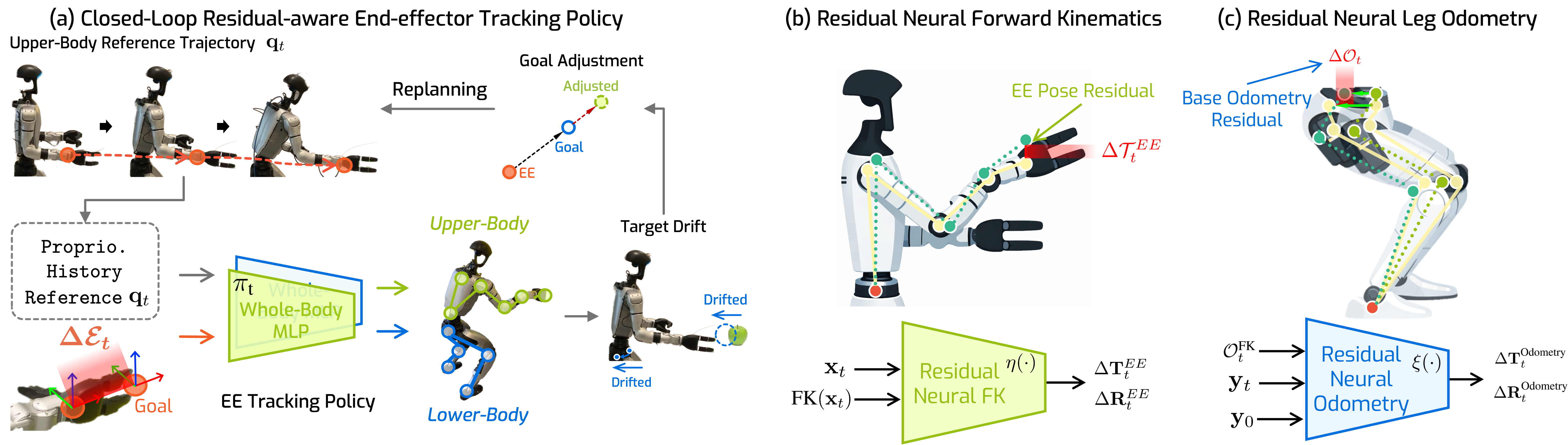
Visual loco-manipulation of arbitrary objects in the wild with humanoid robots requires accurate end-effector (EE) control and a generalizable understanding of the scene via visual inputs (eg, RGB-D images). Existing approaches are based on real-world imitation learning and exhibit limited generalization due to the difficulty in collecting large-scale training datasets. This paper presents a new paradigm, HERO, for object loco-manipulation with humanoid robots that combines the strong generalization and open-vocabulary understanding of large vision models with strong control performance from simulated training. We achieve this by designing an accurate residual-aware EE tracking policy. This EE tracking policy combines classical robotics with machine learning. It uses a) inverse kinematics to convert residual end-effector targets into reference trajectories, b) a learned neural forward model for accurate forward kinematics, c) goal adjustment, and d) replanning. Together, these innovations help us cut down the end-effector tracking error by 3.2x. We use this accurate end-effector tracker to build a modular system for loco-manipulation, where we use open-vocabulary large vision models for strong visual generalization. Our system is able to operate in diverse real-world environments, from offices to coffee shops, where the robot is able to reliably manipulate various everyday objects (eg, mugs, apples, toys) on surfaces ranging from 43cm to 92cm in height. Systematic modular and end-to-end tests in simulation and the real world demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed design. We believe the advances in this paper can open up new ways of training humanoid robots to interact with objects.
Our HERO end-effector tracking control framework has following key components:
@article{dong2026hero,
title={Learning Humanoid End-Effector Control for Open-Vocabulary Visual Loco-Manipulation},
author={Dong, Runpei and Li, Ziyan and He, Xialin and Gupta, Saurabh},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2602.16705},
year={2026}
}